NOTEBOOK
定制Linux内核Syscall
当人工对Linux Kernel做测试时,一般是在应用层编写一个程序,这个程序会执行一些系统调用,然后观察执行的过程和分析执行的结果。
step1:观察现有系统调用
在应用层,编写一个程序,编译并运行
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
const char *message = "Goodbye, System Call!\n";
ssize_t result;
// 使用 syscall 调用 write 系统调用
result = syscall(SYS_write, STDOUT_FILENO, message, strlen(message));
if (result == -1) {
perror("System call failed");
return 1;
}
printf("Wrote %zd bytes using system call.\n", result);
return 0;
}
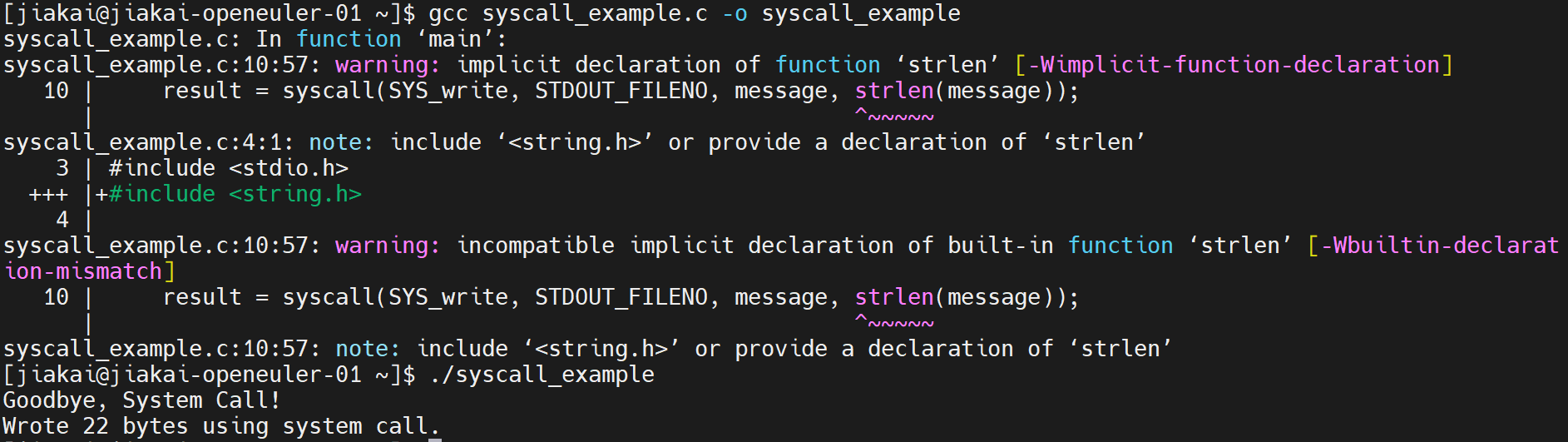
程序中用到了 SYS_write,并且可以推测出与系统调用相关的头文件是unistd.h和sys/syscall.h
查看系统中的unistd.h和sys/syscall.h
可以利用 find . -name unistd.h和 find . -name syscall.h来找到系统中这两个文件,前者与POSIX(Portable Operating System Interface)有关,这里只看后者
sys/syscall.h文件的内容:
#ifndef _SYSCALL_H
#define _SYSCALL_H 1
/* This file should list the numbers of the system calls the system knows.
But instead of duplicating this we use the information available
from the kernel sources. */
#include <asm/unistd.h>
/* The Linux kernel header file defines macros __NR_*, but some
programs expect the traditional form SYS_*. <bits/syscall.h>
defines SYS_* macros for __NR_* macros of known names. */
#include <bits/syscall.h>
#endif
包含asm/unistd.h和bits/syscall.h两个头文件,分别记录了系统调用号和系统调用名称的兼容(SYS_和__NR_)
asm/unistd.h文件的内容:
/*
* AARCH32 interface for ILP32 syscalls.
*/
#if defined(__ILP32__) || defined(__SYSCALL_COMPAT)
#define __ARCH_WANT_SYNC_FILE_RANGE2
#endif
/*
* AARCH64/ILP32 is introduced after the following syscalls were deprecated.
*/
#if !(defined(__ILP32__) || defined(__SYSCALL_COMPAT))
#define __ARCH_WANT_RENAMEAT
#define __ARCH_WANT_SET_GET_RLIMIT
#endif
#define __ARCH_WANT_NEW_STAT
#define __ARCH_WANT_TIME32_SYSCALLS
#define __ARCH_WANT_SYS_CLONE3
#define __ARCH_WANT_MEMFD_SECRET
#include <asm-generic/unistd.h>
包含asm-generic/unistd.h头文件
asm-generic/unistd.h文件的内容:
#include <asm/bitsperlong.h>
/*
* This file contains the system call numbers, based on the
* layout of the x86-64 architecture, which embeds the
* pointer to the syscall in the table.
*
* As a basic principle, no duplication of functionality
* should be added, e.g. we don't use lseek when llseek
* is present. New architectures should use this file
* and implement the less feature-full calls in user space.
*/
#ifndef __SYSCALL
#define __SYSCALL(x, y)
#endif
#if __BITS_PER_LONG == 32 || defined(__SYSCALL_COMPAT)
#define __SC_3264(_nr, _32, _64) __SYSCALL(_nr, _32)
#else
#define __SC_3264(_nr, _32, _64) __SYSCALL(_nr, _64)
#endif
#ifdef __SYSCALL_COMPAT
#define __SC_COMP(_nr, _sys, _comp) __SYSCALL(_nr, _comp)
#define __SC_COMP_3264(_nr, _32, _64, _comp) __SYSCALL(_nr, _comp)
#else
#define __SC_COMP(_nr, _sys, _comp) __SYSCALL(_nr, _sys)
#define __SC_COMP_3264(_nr, _32, _64, _comp) __SC_3264(_nr, _32, _64)
#endif
#define __NR_io_setup 0
__SC_COMP(__NR_io_setup, sys_io_setup, compat_sys_io_setup)
#define __NR_io_destroy 1
__SYSCALL(__NR_io_destroy, sys_io_destroy)
#define __NR_io_submit 2
__SC_COMP(__NR_io_submit, sys_io_submit, compat_sys_io_submit)
#define __NR_io_cancel 3
__SYSCALL(__NR_io_cancel, sys_io_cancel)
#if defined(__ARCH_WANT_TIME32_SYSCALLS) || __BITS_PER_LONG != 32
#define __NR_io_getevents 4
__SC_3264(__NR_io_getevents, sys_io_getevents_time32, sys_io_getevents)
#endif
/* fs/xattr.c */
#define __NR_setxattr 5
__SYSCALL(__NR_setxattr, sys_setxattr)
#define __NR_lsetxattr 6
__SYSCALL(__NR_lsetxattr, sys_lsetxattr)
#define __NR_fsetxattr 7
__SYSCALL(__NR_fsetxattr, sys_fsetxattr)
#define __NR_getxattr 8
__SYSCALL(__NR_getxattr, sys_getxattr)
#define __NR_lgetxattr 9
__SYSCALL(__NR_lgetxattr, sys_lgetxattr)
#define __NR_fgetxattr 10
__SYSCALL(__NR_fgetxattr, sys_fgetxattr)
#define __NR_listxattr 11
__SYSCALL(__NR_listxattr, sys_listxattr)
#define __NR_llistxattr 12
__SYSCALL(__NR_llistxattr, sys_llistxattr)
#define __NR_flistxattr 13
__SYSCALL(__NR_flistxattr, sys_flistxattr)
#define __NR_removexattr 14
__SYSCALL(__NR_removexattr, sys_removexattr)
#define __NR_lremovexattr 15
__SYSCALL(__NR_lremovexattr, sys_lremovexattr)
#define __NR_fremovexattr 16
__SYSCALL(__NR_fremovexattr, sys_fremovexattr)
...
...
记录了每个系统调用的系统调用号,包含的asm/bitsperlong.h头文件用于区分__LP64__和__ILP32__两种不同的编程模型
bits/syscall.h文件的内容:
#ifndef _SYSCALL_H
# error "Never use <bits/syscall.h> directly; include <sys/syscall.h> instead."
#endif
#define __GLIBC_LINUX_VERSION_CODE 394240
#ifdef __NR_FAST_atomic_update
# define SYS_FAST_atomic_update __NR_FAST_atomic_update
#endif
#ifdef __NR_FAST_cmpxchg
# define SYS_FAST_cmpxchg __NR_FAST_cmpxchg
#endif
...
...
用于兼容系统调用名称
以上,我们知道最初的那个C程序中的 SYS_write其实只是一个数字,即系统调用号。
将系统调用号和系统调用联系起来
linux-5.4.285/arch/arm/tools/syscall.tbl中记录了系统调用号和系统调用之间的映射,故而可以得到系统调用名称
#
# Linux system call numbers and entry vectors
#
# The format is:
# <num> <abi> <name> [<entry point> [<oabi compat entry point>]]
#
# Where abi is:
# common - for system calls shared between oabi and eabi (may have compat)
# oabi - for oabi-only system calls (may have compat)
# eabi - for eabi-only system calls
#
# For each syscall number, "common" is mutually exclusive with oabi and eabi
#
0 common restart_syscall sys_restart_syscall
1 common exit sys_exit
2 common fork sys_fork
3 common read sys_read
4 common write sys_write
5 common open sys_open
6 common close sys_close
# 7 was sys_waitpid
8 common creat sys_creat
9 common link sys_link
10 common unlink sys_unlink
11 common execve sys_execve
12 common chdir sys_chdir
13 oabi time sys_time32
14 common mknod sys_mknod
15 common chmod sys_chmod
16 common lchown sys_lchown16
# 17 was sys_break
# 18 was sys_stat
...
...
系统调用实现在哪里
在上面的tbl表中可以找到系统调用名称,具体的实现是在源码的各个目录下,以write系统调用为例,其实现位于fs的read_write.c文件下:
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(write, unsigned int, fd, const char __user *, buf,
size_t, count)
{
return ksys_write(fd, buf, count);
}
step2:定制一个系统调用
定制系统调用有两种方法:
1.以内核模块的形式,定制系统调用,并添加到内核中;
2.将定制的系统调用编写进内核代码中。
这里采用第二种方式,因为第一种方式在尝试insmod时会出现权限问题,猜测可能和qemu不支持kvm相关。
将定制的系统调用编写进内核代码中
编写系统调用代码
在kernel/sys.c文件中实现系统调用代码:
asmlinkage long sys_mysyscall(long num)
{
printk("A Custom Syscall!\n");
printk("The Parameter is %ld.\n", num);
return 0;
}
SYSCALL_DEFINE1(mysyscall, long, num)
{
return sys_mysyscall(num);
}
asmlinkage告诉编译器,函数的参数通过栈传递而非寄存器。
栈传递和寄存器传递的对比:
- 前者兼容性好,几乎所有架构和编译器都支持;后者不同架构的寄存器布局和调用约定可能不同。
- 前者参数存在栈中,方便调试;后者寄存器内容不易直接观察,调试复杂度较高。
- 前者适合参数数量可变或不确定的情况。
- 前者需要内存访问,速度慢;后者寄存器访问速度远快于内存。
分配系统调用号
在arch/x86/entry/syscalls/syscall_64.tbl文件中为系统调用分配系统调用号:
335 64 mysyscall sys_mysyscall
声明系统调用
在include/linux/syscalls.h文件中声明系统调用:
asmlinkage long sys_mysyscall(long num);
编译内核
make
测试结果
在定制的内核中,编写C语言程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
int main()
{
syscall(335, 20250228);
}
编译并运行,通过 dmesg查看运行结果
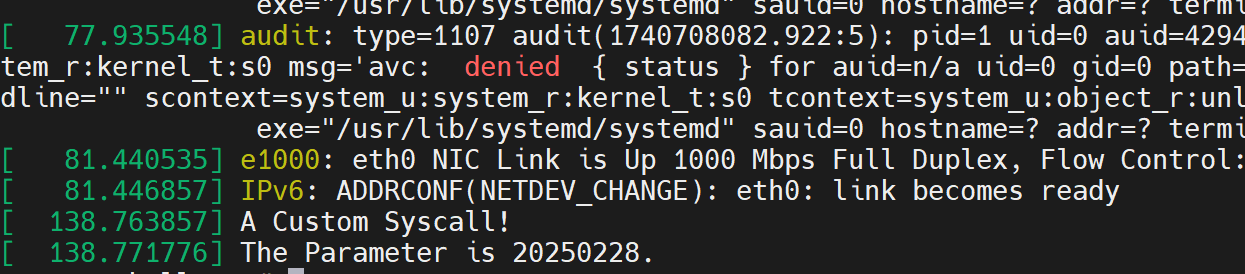
将定制的系统调用编写进内核模块
查看系统调用表在内存中的地址 sudo cat /proc/kallsyms | grep sys_call_table
如果启用了Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR),内核符号的地址会在每次启动时随机化。因此,/proc/kallsyms 中的地址仅在当前运行的内核实例中有效。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/syscalls.h>
#include <linux/linkage.h>
// 定义系统调用号(需要确保未被占用)
#define MY_SYSCALL_NUMBER 335
// 定义系统调用函数
asmlinkage long sys_my_syscall(void) {
printk(KERN_INFO "Custom syscall invoked from kernel module!\n");
return 0;
}
// 替换系统调用表中的条目
//extern void *sys_call_table[];
#define SYSCALL_TABLE_ADDR 0xffffffff9a6031a0
static void **sys_call_table = (void **)SYSCALL_TABLE_ADDR;
// 修改系统调用表的函数
static inline void enable_write_to_ro(void) {
write_cr0(read_cr0() & (~0x10000));
}
static inline void disable_write_to_ro(void) {
write_cr0(read_cr0() | 0x10000);
}
static int __init my_syscall_init(void) {
// 允许写入只读内存区域
enable_write_to_ro();
// 替换系统调用表中的条目
sys_call_table[MY_SYSCALL_NUMBER] = (void *)sys_my_syscall;
// 恢复只读保护
disable_write_to_ro();
printk(KERN_INFO "Custom syscall registered with number %d\n", MY_SYSCALL_NUMBER);
return 0;
}
static void __exit my_syscall_exit(void) {
// 允许写入只读内存区域
enable_write_to_ro();
// 恢复原始系统调用
sys_call_table[MY_SYSCALL_NUMBER] = NULL;
// 恢复只读保护
disable_write_to_ro();
printk(KERN_INFO "Custom syscall unregistered\n");
}
module_init(my_syscall_init);
module_exit(my_syscall_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("A custom system call as a kernel module");
编译得到ko文件后,在insmod时出现报错,推测是权限问题。