NOTEBOOK
Interpreter Mode in Triton
1 Triton的解释执行模式
Triton社区资料:triton/debug/using-the-interpreter
调试Triton程序的一个比较直接和有效的方法是解释器模式。它允许程序员在CPU上运行Triton kernels,并且可以看到kernel中每个操作执行完成后的中间结果。为了使能解释器执行模式,需要设置环境变量 TRITON_INTERPRET为 1。这个设置会让Triton kernels不被编译,而是被解释器通过等价于Triton操作的numpy操作模拟执行。解释器会顺序处理每个kernel实例,同一时刻只会执行一个操作。
基本用法分为两步:1.设置环境变量,export TRITON_INTERPRET=1;2.在Triton kernel中插入print语句,打印想要观察的中间结果。
目前Triton的解释器模式有两个局限:1.不支持bf16,如果原kernel中有bf16,在解释模式下需要转成f32先;2.不支持间接内存访问模式,比如先 ptr = tl.load(ptr)后 x = tl.load(ptr)。
2 一个demo和引发的探究
2-1 demo
先来看一个demo,这个demo程序做的事情是:
- 在GPU上创建一个tensor_x,shape是(4,6),stride是(6,1);
- 通过split方法把tensor_x分为tensor_a和tensor_b,shape分别是(4,2)和(4,4),stride分别是(6,1)和(6,1);
- 定义了一个kernel,接收一个tensor的起始地址和其stride信息。在kernel内,通过tensor起始地址和其stride信息,把数据load到tensor_t内,而后对tensor_t内的每个元素做加一操作,最后写回tensor;
- 对tensor_a和tensor_b分别调用该kernel,执行完毕后观察tensor_x, tensor_a, tensor_b的内容变化;
- 对tensor_a和tensor_b分别执行contiguous操作得到tensor_a_con和tensor_b_con,然后观察tensor_a和tensor_b的元信息变化;
- 对tensor_a_con和tensor_b_con分别调用该kernel,执行完毕后观察tensor_x, tensor_a, tensor_b, tensor_a_con, tensor_b_con的内容变化。
import torch
import triton
import triton.language as tl
def to_cpu_preserve_stride(tensor):
"""完整保留 stride 信息的 CPU 拷贝"""
cpu_tensor = tensor.new_empty(0, device='cpu')
cpu_tensor.set_(
tensor.untyped_storage().cpu(), # 拷贝存储
tensor.storage_offset(), # 保留偏移
tensor.size(), # 保留 shape
tensor.stride() # 保留 stride(包括 0)
)
return cpu_tensor
@triton.jit
def add_one_kernel(
ptr, # 张量指针
stride_0, # 第0维步长
stride_1, # 第1维步长
block_size_0, # 第0维分块大小
block_size_1, # 第1维分块大小
BLOCK_SIZE_0: tl.constexpr,
BLOCK_SIZE_1: tl.constexpr,
):
# 获取当前program的id
pid = tl.program_id(0)
# 计算偏移量
offset_0 = pid * BLOCK_SIZE_0 + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_0)
offset_1 = tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_1)
# 创建mask
mask_0 = offset_0 < block_size_0
mask_1 = offset_1 < block_size_1
# 计算每个元素的地址偏移
offsets = offset_0[:, None] * stride_0 + offset_1[None, :] * stride_1
mask = mask_0[:, None] & mask_1[None, :]
# 加载数据
data = tl.load(ptr + offsets, mask=mask, other=0.0)
# print(f"data = {data}")
# 加1
data = data + 1.0
# 存储回去
tl.store(ptr + offsets, data, mask=mask)
def print_tensor_info(name, tensor):
"""打印张量的元数据信息"""
print(f"\n{name}:")
print(f" Shape: {tensor.shape}")
print(f" Stride: {tensor.stride()}")
print(f" Data pointer: {tensor.data_ptr():#x}")
print(f" Is contiguous: {tensor.is_contiguous()}")
def call_kernel(tensor, block_size_0, block_size_1):
"""调用kernel处理张量"""
stride_0, stride_1 = tensor.stride()
num_programs = (tensor.shape[0] + block_size_0 - 1) // block_size_0
add_one_kernel[(num_programs,)](
tensor,
stride_0,
stride_1,
tensor.shape[0],
tensor.shape[1],
BLOCK_SIZE_0=block_size_0,
BLOCK_SIZE_1=block_size_1,
)
def main():
# 创建原始张量
# original = torch.zeros((4, 6), device='cuda', dtype=torch.float32)
original = torch.arange(24, dtype=torch.float32).reshape(4, 6).cuda()
# original = torch.arange(24, dtype=torch.float32).reshape(4, 6)
# original_cpu = original.cpu()
print("=" * 60)
print("原始张量:")
print(original)
print_tensor_info("原始张量元数据", original)
# print_tensor_info("原始张量元数据(CPU版)", original_cpu)
# ========== 第一阶段:Split后直接使用 ==========
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("第一阶段:Split后直接使用")
print("=" * 60)
# Split成两个张量
tensor1, tensor2 = torch.split(original, [2, 4], dim=1)
# tensor1_cpu = tensor1.cpu()
# tensor2_cpu = tensor2.cpu()
# tensor1_cpu_preserve = to_cpu_preserve_stride(tensor1)
# tensor2_cpu_preserve = to_cpu_preserve_stride(tensor2)
print("\n--- Split后的元数据 ---")
print_tensor_info("tensor1 (4x2)", tensor1)
# print_tensor_info("tensor1_cpu (4x2)", tensor1_cpu)
# print_tensor_info("tensor1_cpu_preserve (4x2)", tensor1_cpu_preserve)
print_tensor_info("tensor2 (4x4)", tensor2)
# print_tensor_info("tensor2_cpu (4x4)", tensor2_cpu)
# print_tensor_info("tensor2_cpu_preserve (4x4)", tensor2_cpu_preserve)
print_tensor_info("原始张量", original)
print("\n--- Split后的内容 ---")
print("tensor1 (4x2):")
print(tensor1)
# print("tensor1_cpu (4x2):")
# print(tensor1_cpu)
# print("tensor1_cpu_preserve (4x2):")
# print(tensor1_cpu_preserve)
print("\ntensor2 (4x4):")
print(tensor2)
# print("tensor2_cpu (4x4):")
# print(tensor2_cpu)
# print("tensor2_cpu_preserve (4x4):")
# print(tensor2_cpu_preserve)
# 调用kernel处理两个张量
print("\n--- 调用kernel处理 tensor1 ---")
call_kernel(tensor1, block_size_0=4, block_size_1=2)
print("--- 调用kernel处理 tensor2 ---")
call_kernel(tensor2, block_size_0=4, block_size_1=4)
print("\n--- Kernel执行后的内容 ---")
print("tensor1 (4x2):")
print(tensor1)
print("\ntensor2 (4x4):")
print(tensor2)
print("\n原始张量:")
print(original)
# ========== 第二阶段:Contiguous后使用 ==========
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("第二阶段:Contiguous后使用")
print("=" * 60)
# 对两个张量做contiguous
tensor1_cont = tensor1.contiguous()
tensor2_cont = tensor2.contiguous()
print("\n--- Contiguous后的元数据 ---")
print_tensor_info("tensor1 (4x2)", tensor1)
print_tensor_info("tensor2 (4x4)", tensor2)
print_tensor_info("tensor1_cont (4x2)", tensor1_cont)
print_tensor_info("tensor2_cont (4x4)", tensor2_cont)
print_tensor_info("原始张量", original)
print("\n--- Contiguous后的内容 ---")
print("tensor1 (4x2):")
print(tensor1)
print("\ntensor2 (4x4):")
print(tensor2)
print("tensor1_cont (4x2):")
print(tensor1_cont)
print("\ntensor2_cont (4x4):")
print(tensor2_cont)
print("\n原始张量:")
print(original)
# 再次调用kernel
print("\n--- 调用kernel处理 tensor1_cont ---")
call_kernel(tensor1_cont, block_size_0=4, block_size_1=2)
print("--- 调用kernel处理 tensor2_cont ---")
call_kernel(tensor2_cont, block_size_0=4, block_size_1=4)
print("\n--- Kernel执行后的内容 ---")
print("tensor1 (4x2):")
print(tensor1)
print("\ntensor2 (4x4):")
print(tensor2)
print("tensor1_cont (4x2):")
print(tensor1_cont)
print("\ntensor2_cont (4x4):")
print(tensor2_cont)
print("\n原始张量:")
print(original)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
2-2 Pytorch API
docs-pytorch : split, contiguous, view, cpu, is_contiguous, stride, copy_
看这些API文档,有助于理解tensor在GPU/CPU上的硬件层面内存布局和软件层面视图。
2-3 GPU运行Triton kernel
============================================================
原始张量:
tensor([[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5.],
[ 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11.],
[12., 13., 14., 15., 16., 17.],
[18., 19., 20., 21., 22., 23.]], device='cuda:0')
原始张量元数据:
Shape: torch.Size([4, 6])
Stride: (6, 1)
Data pointer: 0x751830200000
Is contiguous: True
============================================================
第一阶段:Split后直接使用
============================================================
--- Split后的元数据 ---
tensor1 (4x2):
Shape: torch.Size([4, 2])
Stride: (6, 1)
Data pointer: 0x751830200000
Is contiguous: False
tensor2 (4x4):
Shape: torch.Size([4, 4])
Stride: (6, 1)
Data pointer: 0x751830200008
Is contiguous: False
原始张量:
Shape: torch.Size([4, 6])
Stride: (6, 1)
Data pointer: 0x751830200000
Is contiguous: True
--- Split后的内容 ---
tensor1 (4x2):
tensor([[ 0., 1.],
[ 6., 7.],
[12., 13.],
[18., 19.]], device='cuda:0')
tensor2 (4x4):
tensor([[ 2., 3., 4., 5.],
[ 8., 9., 10., 11.],
[14., 15., 16., 17.],
[20., 21., 22., 23.]], device='cuda:0')
--- 调用kernel处理 tensor1 ---
--- 调用kernel处理 tensor2 ---
--- Kernel执行后的内容 ---
tensor1 (4x2):
tensor([[ 1., 2.],
[ 7., 8.],
[13., 14.],
[19., 20.]], device='cuda:0')
tensor2 (4x4):
tensor([[ 3., 4., 5., 6.],
[ 9., 10., 11., 12.],
[15., 16., 17., 18.],
[21., 22., 23., 24.]], device='cuda:0')
原始张量:
tensor([[ 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6.],
[ 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12.],
[13., 14., 15., 16., 17., 18.],
[19., 20., 21., 22., 23., 24.]], device='cuda:0')
============================================================
第二阶段:Contiguous后使用
============================================================
--- Contiguous后的元数据 ---
tensor1 (4x2):
Shape: torch.Size([4, 2])
Stride: (6, 1)
Data pointer: 0x751830200000
Is contiguous: False
tensor2 (4x4):
Shape: torch.Size([4, 4])
Stride: (6, 1)
Data pointer: 0x751830200008
Is contiguous: False
tensor1_cont (4x2):
Shape: torch.Size([4, 2])
Stride: (2, 1)
Data pointer: 0x751830200200
Is contiguous: True
tensor2_cont (4x4):
Shape: torch.Size([4, 4])
Stride: (4, 1)
Data pointer: 0x751830200400
Is contiguous: True
原始张量:
Shape: torch.Size([4, 6])
Stride: (6, 1)
Data pointer: 0x751830200000
Is contiguous: True
--- Contiguous后的内容 ---
tensor1 (4x2):
tensor([[ 1., 2.],
[ 7., 8.],
[13., 14.],
[19., 20.]], device='cuda:0')
tensor2 (4x4):
tensor([[ 3., 4., 5., 6.],
[ 9., 10., 11., 12.],
[15., 16., 17., 18.],
[21., 22., 23., 24.]], device='cuda:0')
tensor1_cont (4x2):
tensor([[ 1., 2.],
[ 7., 8.],
[13., 14.],
[19., 20.]], device='cuda:0')
tensor2_cont (4x4):
tensor([[ 3., 4., 5., 6.],
[ 9., 10., 11., 12.],
[15., 16., 17., 18.],
[21., 22., 23., 24.]], device='cuda:0')
原始张量:
tensor([[ 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6.],
[ 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12.],
[13., 14., 15., 16., 17., 18.],
[19., 20., 21., 22., 23., 24.]], device='cuda:0')
--- 调用kernel处理 tensor1_cont ---
--- 调用kernel处理 tensor2_cont ---
--- Kernel执行后的内容 ---
tensor1 (4x2):
tensor([[ 1., 2.],
[ 7., 8.],
[13., 14.],
[19., 20.]], device='cuda:0')
tensor2 (4x4):
tensor([[ 3., 4., 5., 6.],
[ 9., 10., 11., 12.],
[15., 16., 17., 18.],
[21., 22., 23., 24.]], device='cuda:0')
tensor1_cont (4x2):
tensor([[ 2., 3.],
[ 8., 9.],
[14., 15.],
[20., 21.]], device='cuda:0')
tensor2_cont (4x4):
tensor([[ 4., 5., 6., 7.],
[10., 11., 12., 13.],
[16., 17., 18., 19.],
[22., 23., 24., 25.]], device='cuda:0')
原始张量:
tensor([[ 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6.],
[ 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12.],
[13., 14., 15., 16., 17., 18.],
[19., 20., 21., 22., 23., 24.]], device='cuda:0')
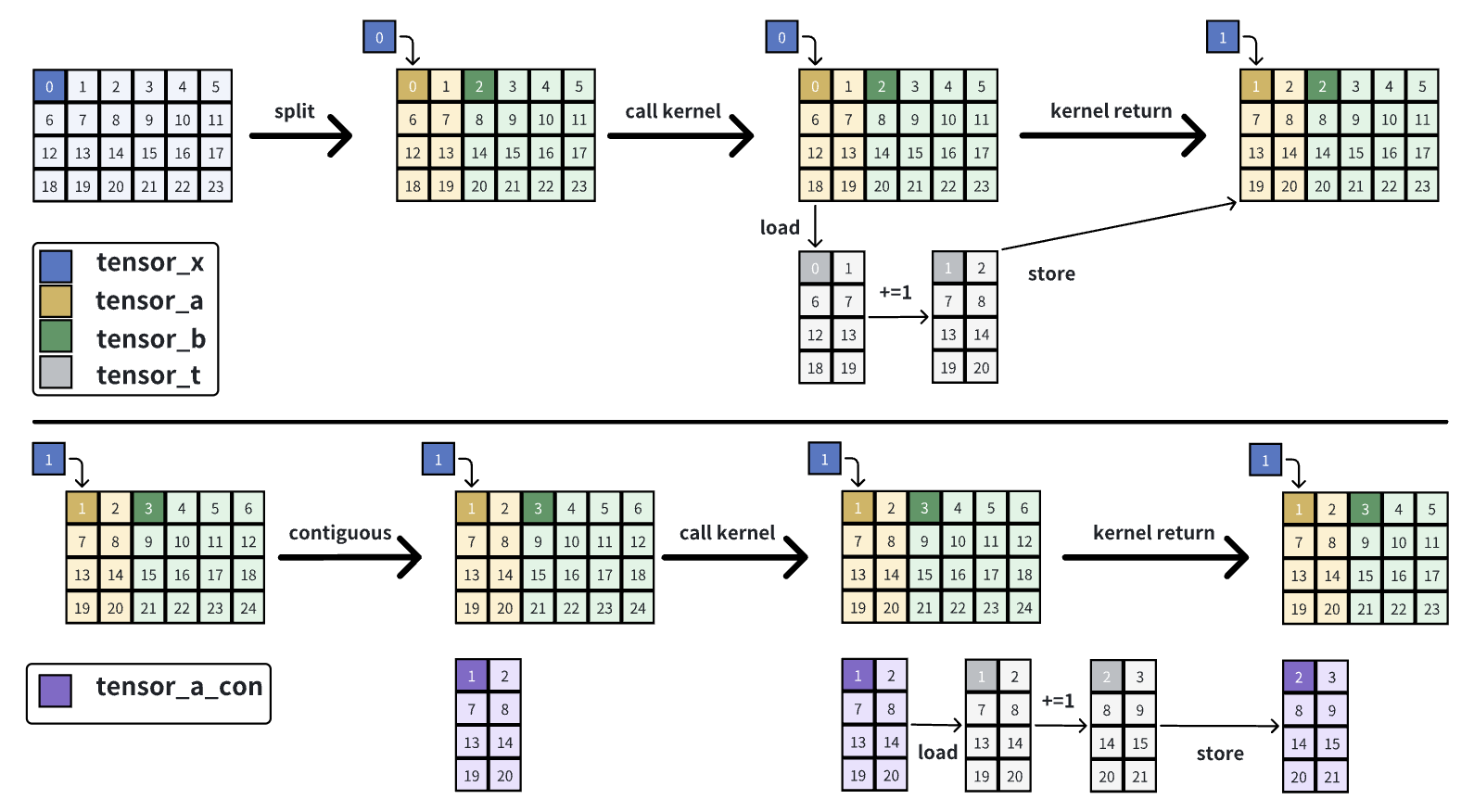
- 对tensor_x做split得到tensor_a和tensor_b:在GPU上只有一块数据,tensor_x, tensor_a, tensor_b都指向这一块数据;三者shape不同、stride相同;
- 对tensor_a调用kernel:在kernel内会把tensor_a的数据load到tensor_t,然后对tensor_t做加一操作,而后store回tensor_a;
- 观察:对tensor_a调用kernel,tensor_x所指的那块数据变化了。
- 对tensor_a调用contiguous:在GPU上会把tensor_a的数据复制一份,shape不变,stride由(6,1)变为(2,1),得到tensor_a_con;
- 对tensor_a_con调用kernel:在kernel内会把tensor_a_con的数据load到tensor_t,然后对tensor_t做加一操作,而后store回tensor_a_con;
- 观察:可以看到tensor_x所指的那块数据没有变化。
2-4 CPU解释执行Triton kernel
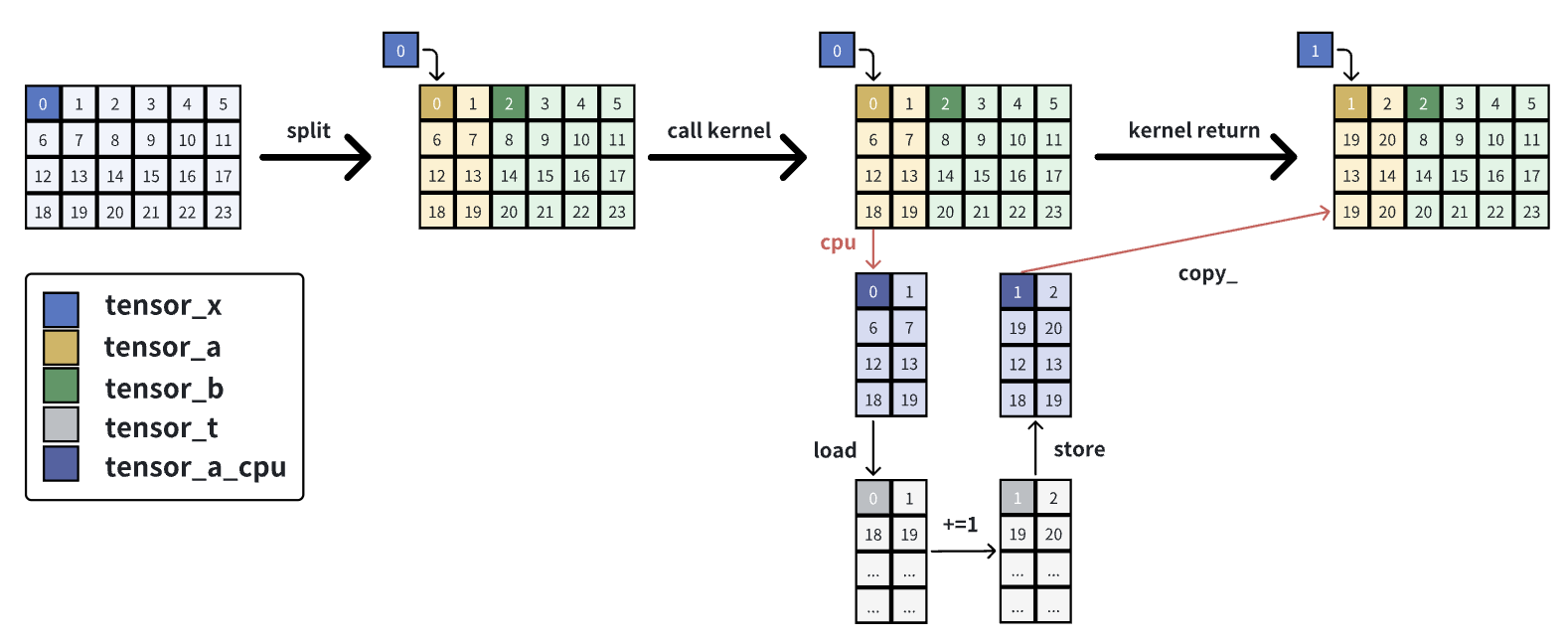
- 对tensor_x做split得到tensor_a和tensor_b:在GPU上只有一块数据,tensor_x, tensor_a, tensor_b都指向这一块数据;三者shape不同、stride相同;
- 对tensor_a调用kernel:在调用kernel之前,会把位于GPU的tensor_a通过.cpu()方法复制一份到CPU得到tensor_a_cpu,tensor_a和tensor_a_cpu的区别在于后者是contiguous的,即二者stride不同,当计算完毕后,会通过.copy_方法把位于CPU的tensor_a_cpu写回到tensor_a上。在kernel内,会按照tensor_a的stride把tensor_a_cpu给load进tensor_t,然后对tensor_t做加一操作,并按照tensor_a的stride进行store,从而写入tensor_a_cpu,当kernel执行完毕后,会把tensor_a_cpu的值写回tensor_a。copy_方法可以正确处理src和self的stride不同的情况,而copy不行。
contiguous的部分就不说了,和在GPU上执行差别不大。
2-5 总结
当使用Triton的Interpret模式去执行kernel时,且该kernel中的某个tensor参数是非contiguous的,那么在triton的b99a3006d8e45bc3a588aad82a513e1cc9c7c692之前都是会出现上述问题的,这是由.cpu()方法导致的,该commit对这个问题做了修复。
.cpu()
->
def to_cpu_preserve_stride(tensor):
cpu_tensor = tensor.new_empty(0, device='cpu')
cpu_tensor.set_(
tensor.untyped_storage().cpu(), # 拷贝存储
tensor.storage_offset(), # 保留偏移
tensor.size(), # 保留 shape
tensor.stride() # 保留 stride
)
return cpu_tensor